In fiscal year 2022 (FY22), the International Space Station (ISS) National Laboratory made great strides in its mission to return value to the nation and enable a sustainable economy in low Earth orbit (LEO). This year, NASA extended its Cooperative Agreement with CASIS to manage the ISS National Lab through 2027. The first two decades of ISS operations were dedicated to assembling the space station and validating its capabilities. Now, this third decade is the decade of results. These results are crucial for demonstrating the value of space-based research and development (R&D) to support the establishment of and transition to future commercial LEO destinations.
In terms of results, FY22 was a record-setting year for the ISS National Lab. This year, nearly 50 peer-reviewed articles related to ISS National Lab-sponsored research were published—the highest number ever identified in a fiscal year. Close to 70 percent of these publications were related to fundamental science funded by the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF), building a solid knowledge base to enable future applied R&D. Additionally, in FY22, two patents were granted to companies for intellectual property related to their space-based research, and four commercial products stemmed from ISS National Lab-sponsored R&D. One of these products, the virtual reality exhibit “ISS Experience: The Infinite,” attracted 174,000 viewers as it traveled to multiple U.S. cities.
“The NASA partnership with the ISS National Lab has never been stronger. NASA was pleased to extend our Cooperative Agreement with CASIS to ensure the ISS National Lab’s contributions to the decade of results will continue. This extension provides continuity for the user community while we work together to evolve the national lab model later in the decade to support the transition to commercial low Earth orbit destinations.”
– Robyn Gatens, NASA Director of the International Space Station
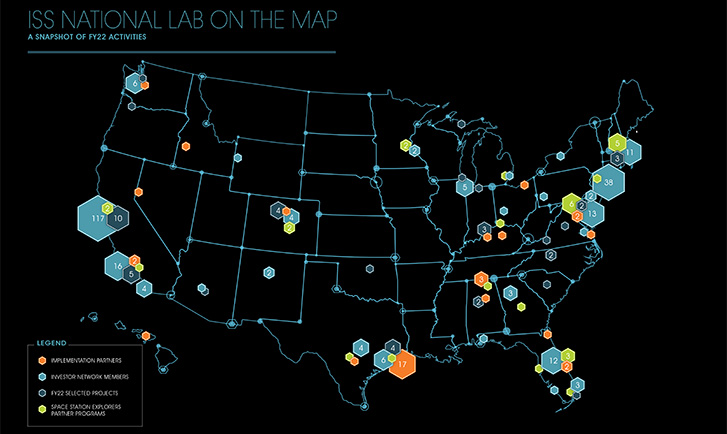
In FY22, the ISS National Lab continued to expand the LEO marketplace by driving demand in key R&D areas, supporting supply-side growth, and fostering increased investment into the LEO economy. This year, 75 ISS National Lab-sponsored payloads launched to station. Of those, 85 percent represented research from commercial entities, underscoring the continued strong demand for space-based R&D among industry users. The ISS National Lab selected 46 new projects for flight in FY22 and achieved a 30 percent improvement in the average time from solicitation close to notification of selection compared with FY21. Of the newly selected projects, 60 percent were from new-to-space users, demonstrating the success of ISS National Lab research solicitations in reaching new communities.
CASIS continues to work with other government agencies to bring in funding to support ISS National Lab-sponsored research in both the physical and life sciences. In FY22, more than 25 percent of newly selected projects were from annual joint solicitations with NSF. In total, through multiyear partnerships with CASIS, NSF and the National Institutes of Health (NIH) have provided more than $40 million in funding, supporting nearly 60 ISS National Lab-sponsored investigations.
On the supply side, the ISS National Lab continued to facilitate business growth in the diverse community of companies and organizations that provide services related to payload development. There are now 39 Implementation Partners, with the addition of one new partner this year. In FY22, more than 80 percent of CASIS funding was used to cover Implementation Partner costs for investigators conducting ISS National Lab-sponsored research. The 24 ISS National Lab commercial facilities now include launch-on-demand facilities that are highly utilized. Additionally, Implementation Partner Axiom Space achieved a historic first with the launch of the first all-private astronaut crew on the Axiom Mission 1, which executed more than 25 ISS National Lab-sponsored payloads.
In FY22, the all-time cumulative amount of capital raised by startups following flight of ISS National Lab-sponsored projects reached more than $1.8 billion. The first quarter of FY22 was record-setting, with more than $550 million of private and public capital and grant funding raised by startups postflight. Additionally, the ISS National Lab expanded its investor network, reaching nearly 280 members in FY22. To date, CASIS has facilitated more than 1,200 capital introductions between startups and investors in this network.
“The ISS National Lab User Advisory Committee, along with the overall user community and the general public, has utilized a new web portal set up by CASIS to facilitate communication, allowing stakeholders to offer feedback, ask questions, share concerns, and help improve how users access the unique research facilities on the ISS. We look forward to continued success in providing the scientific community with access to R&D in low Earth orbit while balancing the limited resources in demand by our user community.”
– Douglas Matson, ISS National Lab User Advisory Committee Chair
As a key part of its mission, the ISS National Lab works to shape the next generation of leaders essential to the future LEO economy. In FY22, more than 9.5 million people participated in ISS National Lab educational partner programs. To further engage educators and students, the ISS National Lab released Expedition Space Lab, a new online tool that provides educators easy access to ISS-related lessons and resources. Additionally, in FY22, the ISS National Lab selected recipients of the inaugural James A. Abrahamson Space Leader Fellowship, which prepares college students for careers in the space industry.
FY22 marked the 11th annual ISS Research and Development Conference (ISSRDC), held in person for the first time since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic. ISSRDC 2022, held in Washington, D.C., brought together researchers, entrepreneurs, policymakers, investors, and others in the space community to discuss the next decade of space station R&D.
This year, CASIS expanded its board of directors, welcoming four new board members: Margaret Jenny, John Sheets, Waleed Abdalati (former NASA chief scientist), and David Radzanowski (former NASA chief financial officer). Additionally, Francisco Cordova joined CASIS as the chief operating officer for the ISS National Lab, and Michael Roberts was named ISS National Lab chief scientist. Throughout the year, the ISS National Lab User Advisory Committee (UAC), which held two public meetings in FY22, provided recommendations to the CASIS chief executive officer on revisions to the committee’s original charter as well as guidance regarding the allocation and utilization of ISS National Lab resources.
A Personal Note From Ramon Lugo, Principal Investigator and CEO of CASIS:
I want to express my thanks not only to the CASIS team but also to our stakeholder community for helping us achieve the results documented in this Annual Report. It has been said by many that little of importance can be accomplished by a single person or organization. It is only through strong partnerships that we collectively find new and innovative ways to use the ISS to solve problems and generate solutions for humankind. We continue to work closely with NASA, our research and technology development community, the investment community, and commercial partners to create new opportunities to impact humanity. I look forward to the new year, as we have big plans and expect to engage the space community in helping us prepare the ISS National Lab for the transition to commercial LEO destinations. Please take the time to read this report, and feel free to share it with family, friends, and colleagues.